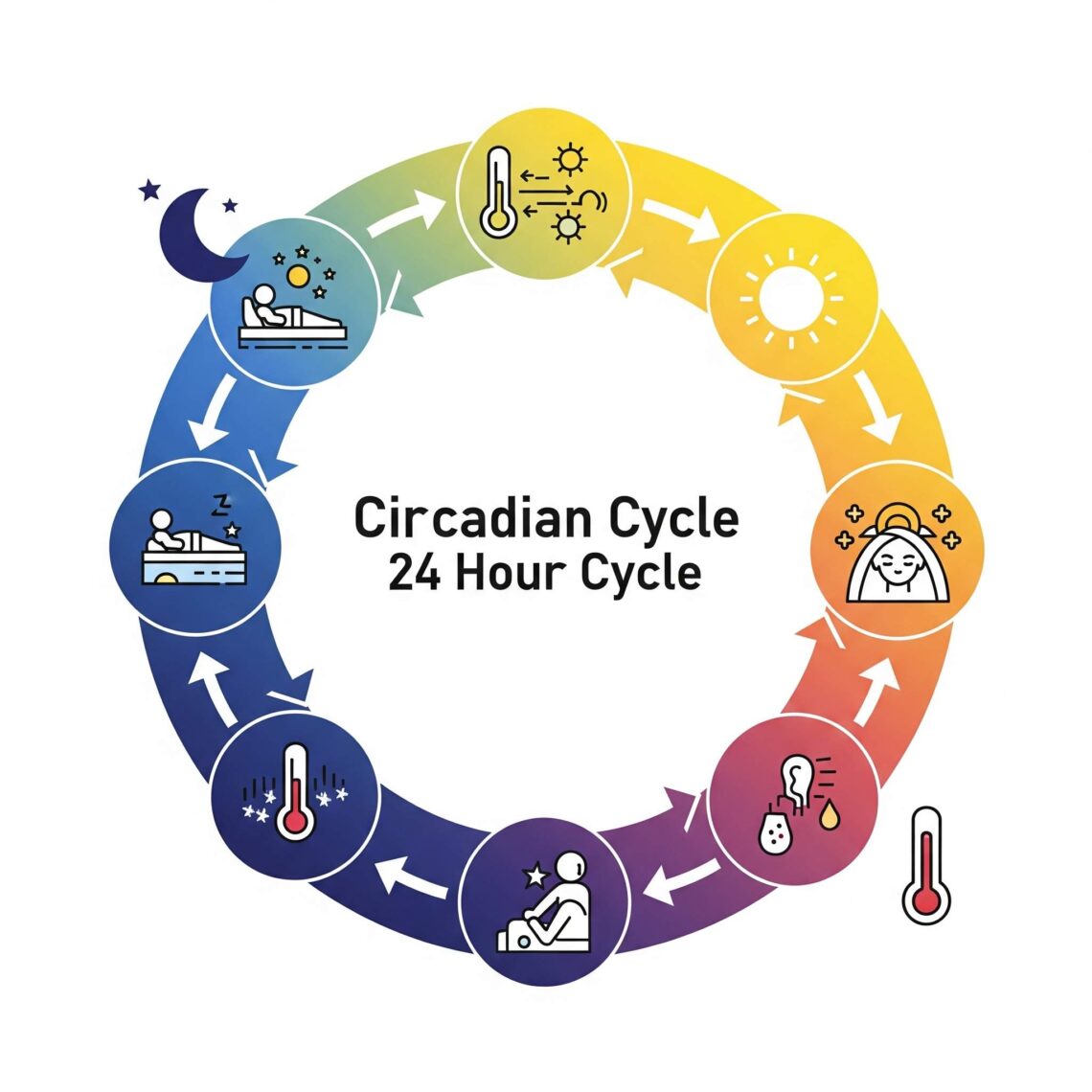
Circadian entrainment refers to the synchronization of your circadian rhythm—your internal 24-hour biological clock—with environmental signals called zeitgebers (German for “time givers”). The most powerful zeitgeber is natural light, but other cues include meal timing, physical activity, and temperature. Your brain’s suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), located in the hypothalamus, acts as the master clock. It receives information from the eyes and adjusts the timing of sleep, hormone production, and body temperature accordingly. When light hits the retina in the morning, it signals the SCN to suppress melatonin and increase alertness. As evening approaches and light decreases, melatonin levels rise, preparing your…
-
-
The circadian cycle is a vital internal process that regulates your body’s functions on a roughly 24-hour schedule. This biological rhythm controls sleep-wake patterns, hormone secretion, metabolism, and even cognitive functions. Understanding the it allows you to align your lifestyle with your body’s natural timing, improving health and daily performance. What Is the Circadian Cycle? The term circadian cycle comes from the Latin circa (around) and diem (day), meaning a roughly 24-hour cycle. It is present in nearly all living organisms, including humans, animals, and plants. In humans, the circadian cycle influences many processes beyond sleep, such as body temperature,…